Introduction:
In the realm of machining, precision is paramount. The ability to produce accurate and high-quality parts hinges on the precision of the machine tools used in the manufacturing process. One critical aspect of this precision is ensuring that the spindle is running true to center. Tool holder test bars play a vital role in this endeavor, serving as a reliable means to gauge and maintain the accuracy of machine spindles.
The Importance of Spindle Accuracy:
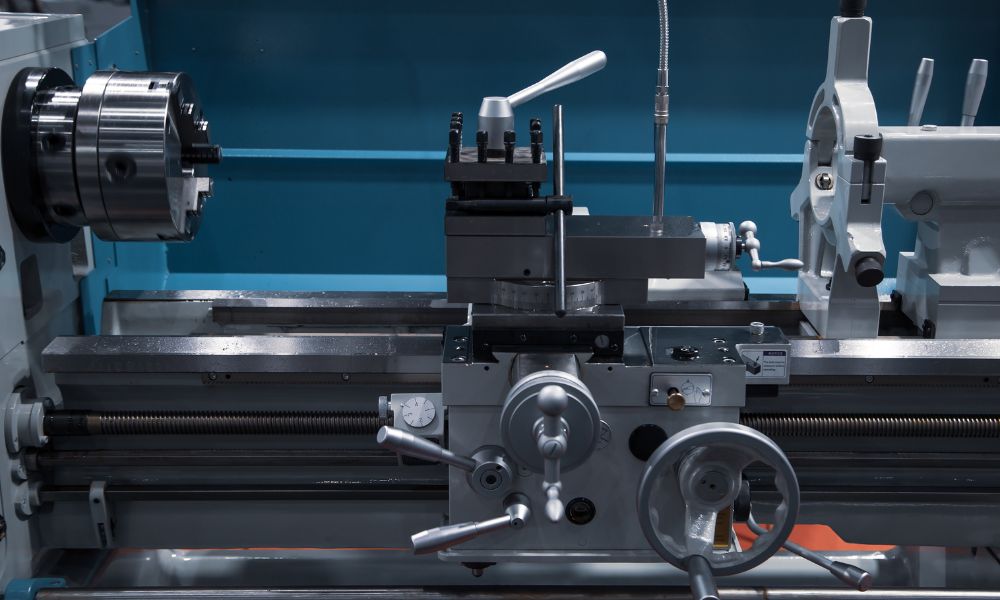
A spindle is the heart of any machining center, responsible for rotating the cutting tool at high speeds. Even the slightest deviation from the centerline can result in dimensional inaccuracies, surface finish issues, and, ultimately, compromised product quality. To address this, machinists employ tool holder test bars as a proactive measure to verify and correct any misalignment.
Tool Holder Test Bars Explained:
Tool holder test bars are precision-engineered cylindrical bars made from high-quality materials such as hardened steel. These bars are designed to be inserted into the machine tool’s spindle, replicating the path of the cutting tool during actual machining. The ability to replicate these conditions is crucial for accurate spindle alignment.
The Testing Process:
- Insertion of the Test Bar:
Machinists begin by securing the tool holder test bar in the machine spindle using an appropriate tool holder. It is crucial to ensure that the test bar is properly seated and tightly secured. - Rotation and Observation:
With the test bar in place, the spindle is rotated at a moderate speed. Machinists carefully observe any deviations or wobbling in the rotation of the test bar. Any irregularities detected indicate potential misalignment issues with the spindle. - Adjustments and Corrections:
If misalignment is identified, machinists can take corrective measures using adjustment features on the machine tool. This may involve aligning the spindle axis or adjusting the bearings to bring the spindle back to its true center. - Re-Testing:
After adjustments are made, machinists re-insert the test bar and repeat the process to ensure that the spindle is now running true to center.
Comprehension Test:
- Why is spindle accuracy crucial in machining?
a) It has no impact on the quality of the final product.
b) It ensures dimensional accuracy and high-quality surface finish.
c) It speeds up the machining process. - What material are tool holder test bars typically made from?
a) Plastic
b) Aluminum
c) Hardened steel - What is the purpose of rotating the test bar during the testing process?
a) To create sparks
b) To observe any deviations or wobbling
c) To generate heat
Answer Key:
- b) It ensures dimensional accuracy and high-quality surface finish.
- c) Hardened steel
- b) To observe any deviations or wobbling